To get a better grasp of double declining balance, spend a little time experimenting with this double declining balance calculator. It’s a good way to see the formula in action—and understand what kind of impact double declining depreciation might have on your finances. DDB is best used for assets that lose value quickly and generate more revenue in their early years, such as vehicles, computers, and technology equipment. This method aligns depreciation expense with the asset’s higher productivity and faster obsolescence in the initial period. DDB is a specific form of declining balance depreciation that doubles the straight-line rate, accelerating expense recognition.
- In this lesson, I explain what this method is, how you can calculate the rate of double-declining depreciation, and the easiest way to calculate the depreciation expense.
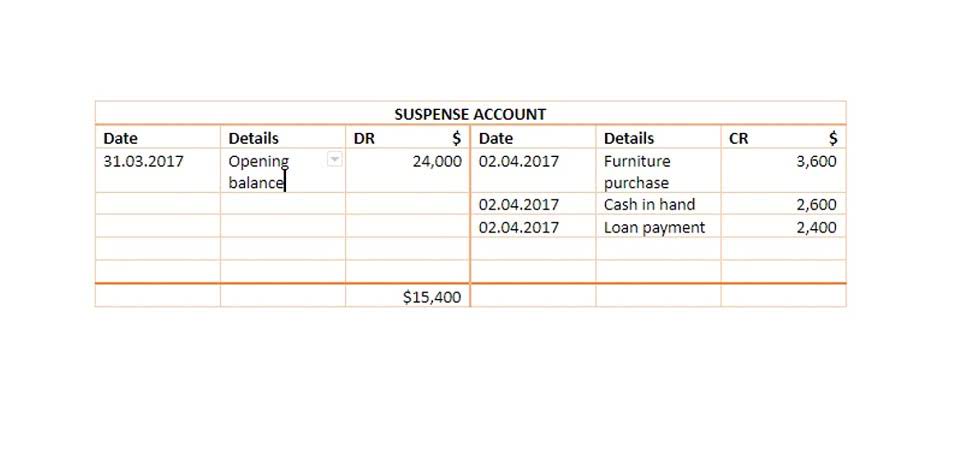
- However, if the company chose to use the DDB depreciation method for the same asset, that percentage would increase to 20%.
- This happens because of the matching principle from GAAP, which says expenses are recorded in the same accounting period as the revenue that is earned as a result of those expenses.
- In the case of 200%, the asset will depreciate twice as fast as it would under straight-line depreciation.
- Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
What Does the Declining Balance Method Tell You?
Since public companies are incentivized to increase shareholder value (and thus, their share price), it is often in their best interests to recognize depreciation more gradually using the straight-line method. In particular, companies that are publicly traded understand that investors in the market could perceive lower profitability negatively. However, one counterargument is that it often takes time for companies to utilize the full capacity of an asset until some time has passed. Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance.

What are other accelerated depreciation methods?
- We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site.
- Our team is ready to learn about your business and guide you to the right solution.
- Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts.
- Sometimes, these are combined into a single line such as “PP&E net of depreciation.”
- Depreciation is the act of writing off an asset’s value over its expected useful life, and reporting it on IRS Form 4562.
- When changing depreciation methods, companies should carefully justify the change and adhere to accounting standards and tax regulations.
- However, the 20% is multiplied times the fixture’s book value at the beginning of the year instead of the fixture’s original cost.
Of course, the pace at which the depreciation expense is recognized under accelerated depreciation methods declines over time. The formula used to calculate annual depreciation expense under the double declining method is as follows. The steps to determine the annual depreciation expense under the double declining method are as follows. The DDB depreciation method offers businesses a strategic approach to accelerate depreciation. When it comes to taxes, this approach can help your business reduce its tax liability during the crucial early years of asset ownership. Depreciation is an accounting process by which a company allocates an asset’s cost throughout its useful life.
Double Declining Balance Method Calculator
We empower accounting teams to work more efficiently, accurately, and collaboratively, enabling them to add greater value to their organizations’ accounting processes. Our Financial Close Software is designed to create detailed month-end close plans with specific close tasks that https://www.bookstime.com/ can be assigned to various accounting professionals, reducing the month-end close time by 30%. The workspace is connected and allows users to assign and track tasks for each close task category for input, review, and approval with the stakeholders. It allows users to extract and ingest data automatically, and use formulas on the data to process and transform it.

Double Declining Balance Method (DDB)
If you’re brand new to the concept, open another tab and check out our complete guide to depreciation. Then come back here—you’ll have the background knowledge you need to learn about double declining balance. Multiply the straight line depreciation rate by 2 to get the double declining depreciation rate. The straight-line depreciation method simply subtracts the salvage value from the cost of the double declining balance method asset and this is then divided by the useful life of the asset.

Step 4: Compute the Final Year Depreciation Expense
To calculate the double-declining depreciation expense for Sara, we first need to figure out the depreciation rate. In the accounting period in which an asset is acquired, the depreciation expense calculation needs to account for the fact that the asset has been available only for a part of the period (partial year). Unlike the straight-line method, the double-declining method depreciates a higher portion of the asset’s cost in the early years and reduces the amount of expense charged in later years.
When to use the DDB depreciation method
- In case of any confusion, you can refer to the step by step explanation of the process below.
- Each method has its advantages, suited to different types of assets and financial strategies.
- As a hypothetical example, suppose a business purchased a $30,000 delivery truck, which was expected to last for 10 years.
- Consider a widget manufacturer that purchases a $200,000 packaging machine with an estimated salvage value of $25,000 and a useful life of five years.
- If the company chose to deduct 10% of the asset’s value each year for ten years under straight-line depreciation, the amount of depreciation per year would only change slightly.
Depreciation rates used in the declining balance method could be 150%, 200% (double), or 250% of the straight-line rate. When the depreciation rate for the declining balance method is balance sheet set as a multiple, doubling the straight-line rate, the declining balance method is effectively the double-declining balance method. Over the depreciation process, the double depreciation rate remains constant and is applied to the reducing book value each depreciation period. Suppose, however, that the company had been using an accelerated depreciation method, such as double-declining balance depreciation.


